Reproductive Medicine
Infertility options for having a family
 For couples wanting a family, it’s never easy to hear that you have reproductive difficulties. It’s also more common than many people realise – as many as 25% of couples in their reproductive years experience infertility.
For couples wanting a family, it’s never easy to hear that you have reproductive difficulties. It’s also more common than many people realise – as many as 25% of couples in their reproductive years experience infertility.
Fortunately there are several effective routes open to help you fulfill your desire for a child.
The first port of call when dealing with childlessness is to medically determine whether your challenges are a result of sterility, which is the inability to conceive within one year of having regular intercourse, or infertility, in which the same definition for sterility applies with the addition of recurrent miscarriages.
 When it comes to reproductive medicine, it’s best to take a holistic approach, which includes taking the medical history of both partners, a physical examination, special investigations where necessary and surgical procedures where necessary, which may include hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
When it comes to reproductive medicine, it’s best to take a holistic approach, which includes taking the medical history of both partners, a physical examination, special investigations where necessary and surgical procedures where necessary, which may include hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
Your reproductive medicine specialist will also consider lifestyle of both partners such as smoking, which affects sperm motility and egg implantation; weight, which affects sperm count, fertilisation and likelihood of miscarriage; fitness, medication, medical conditions and age, with likelihood of abnormal embryos increasing with age.
Once fertility treatment begins, your doctor will explore various options with you, which include ovulation induction through injection or tablets; artificial insemination that is either homologous or via donor; GIFTT or Gamete Intrafallopian Tube Transfer although this method isn’t often used as it’s less effective than artificial insemination; ZIFTT or Zygote intrafallopian Tube Transfer, which is also seldom performed; and finally IVF or In Vitro Fertilisation.
Understanding IVF
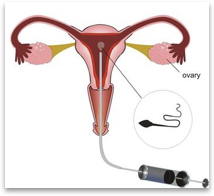 This is a process of conceiving outside of the human body, wherein an ovum is fertilised with sperm in a laboratory. You get two kinds of IVF treatment, namely conventional IVF and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injunction (ICSI) IVF. These methods are suited to cases where there is an issue with the fallopian tubes, male infertility, endometriosis, advanced maternal age, unexplained infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, genetic abnormalities, ovary dysfunction, surrogacy and female donor gametes.
This is a process of conceiving outside of the human body, wherein an ovum is fertilised with sperm in a laboratory. You get two kinds of IVF treatment, namely conventional IVF and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injunction (ICSI) IVF. These methods are suited to cases where there is an issue with the fallopian tubes, male infertility, endometriosis, advanced maternal age, unexplained infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, genetic abnormalities, ovary dysfunction, surrogacy and female donor gametes.
Typically, IVF success rates increase with each cycle with 40% success for first cycle transfer, 45-50% for second cycle transfer and 50-60% for third cycle transfer.
How IVF works
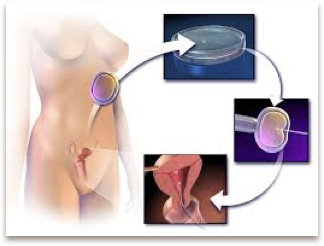 After ovulation induction, ovum are collected as is a sample of sperm. Sperm is washed and introduced to the ovum for fertilisation. Once fertilization has occurred, the embryos are cultured while they undergo their first few divisions. When an embryo is deemed viable, it then moves to vitrification (freezing), PGD testing to screen for genetic abnormalities and and transfer. You will then be tested 10 to 16 days after transfer for implantation.
After ovulation induction, ovum are collected as is a sample of sperm. Sperm is washed and introduced to the ovum for fertilisation. Once fertilization has occurred, the embryos are cultured while they undergo their first few divisions. When an embryo is deemed viable, it then moves to vitrification (freezing), PGD testing to screen for genetic abnormalities and and transfer. You will then be tested 10 to 16 days after transfer for implantation.
Other factors influencing IVF success rates
 Age is a primary factor to take into consideration. A woman over the age of 35 has fewer and lower quality eggs. Success rates for over 35s is around 40%, while for over 42 is drastically lower at 4%.
Age is a primary factor to take into consideration. A woman over the age of 35 has fewer and lower quality eggs. Success rates for over 35s is around 40%, while for over 42 is drastically lower at 4%.
If you have had previous pregnancies with your current partner through IVF, there is a greater probability of IVF success. Conversely, recurrent miscarriage or a different partner may reduce the chances of IVF success.
It must be noted that certain circumstances can make fulfilling the dream of a child more challenging. This includes severe male infertility, uterine congenital abnormalities, fibroid tumours, ovarian dysfunction such as low ovarian reserve, large amounts or extended use of ovarian stimulation drugs, both partners being infertile, as well as the length of time being infertile.
In more difficult cases of fertility, donor eggs from a younger woman can increase the chances of success to 55%.
Lifestyle changes can have significant impact on the success rate of IVF treatment. It’s recommended that you stop smoking at least three months before attempting IVF treatment as smoking requires higher doses of fertility drugs, implantation rates are lower in smokers, smoking women require almost twice as many IVF attempts for success, while being obese or underweight can both hamper IVF success.
The Future of Fertility
 This is an exciting and dynamic field of medical research and practice, with each year bringing new advances and improved practises. Some exciting treatments being developed include nuclear and cyto transfer, stem cell therapy and reproductive choices for treated cancer patients.
This is an exciting and dynamic field of medical research and practice, with each year bringing new advances and improved practises. Some exciting treatments being developed include nuclear and cyto transfer, stem cell therapy and reproductive choices for treated cancer patients.
If you have questions regarding your fertility or how Dr Wynand E van Tonder can help you on your road to being parents, contact us .
